The Best Hard Drive 2024
The best hard drive in 2024 is Gen 5 NVMe, although not technically a hard drive.
It’s important to check if your device has the required motherboard slot to support this disk – although it’s not technically a disk.
How To Choose The Best Hard Drive
This article only considers HDDs (Hard Disk Drives), SSD’s (Solid State Drives) and NVMe (Non Volatile Memory Express), other disk types are available.
Choosing the best hard drive can feel overwhelming with the myriad of options available today. Whether you’re upgrading your existing system or building a new one, the right hard drive can significantly impact performance, storage capacity, and overall user experience.
What types of Hard Drive are available?
We’re going to limit this to the two main types of hard disk available today,: HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and SSD (Solid State Drive).
In modern computing, SSDs are often preferred for their speed and durability, while HDDs are still used for bulk storage solutions where cost-effectiveness is crucial.

SATA HDD Disk
- Mechanism: HDDs use spinning disks (platters) to read and write data. They have mechanical parts including a read/write head that moves across the platters.
- Speed: Typically slower than SSDs due to the mechanical movements required to read/write data.
- Capacity: Generally offers larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte compared to SSDs.
- Durability: More susceptible to physical damage due to moving parts.
- Lifespan: Limited by the wear and tear of the mechanical parts.
- Usage: Suitable for storing large amounts of data where speed is less critical, such as in servers, desktops, and for archival purposes.

SATA SSD Disk
- Mechanism: SSDs use flash memory to store data, with no moving parts. Data is accessed electronically, which makes the process faster.
- Speed: Significantly faster read and write speeds compared to HDDs, leading to quicker boot times, faster file transfers, and improved overall system performance.
- Capacity: More expensive per gigabyte, leading to higher costs for larger capacities.
- Durability: More resistant to physical shock and damage since they lack moving parts.
- Lifespan: Generally, SSDs have a finite number of write cycles, but modern SSDs have improved durability.
- Usage: Ideal for operating systems, applications, and tasks requiring high-speed data access, such as gaming, video editing, and running virtual machines.
So what is NVMe?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is not a disk type, it is the protocol used to access non-volatile storage media (disk) – normally the disk is an SSD.
An SSD Drive in an NVMe configuration will perform much faster than an SSD connected to AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) which is the interface that communicates with Serial ATA (SATA) disks.
An NVMe SSD can transfer data at up to 10Gbps, and theoretically higher, while the same SSD connected via SATA 3 would be limited to 6Gbps.
NVMe SSD Disk
- Speed: NVMe SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to SATA SSDs and HDDs.
- Low Latency: NVMe provides lower latency, resulting in quicker data access and improved performance for high-speed applications
- Optimised Protocol: NVMe is designed specifically for flash memory, reducing overhead and increasing efficiency.
- Parallelism: Supports multiple command queues and commands per queue, maximising the performance of multi-core processors.
Which hard drive is the fastest?
Determining the fastest hard drive involves considering several factors, including read/write speeds, interface types, and the technology used (SSD vs HDD).
SSDs Are Much Faster Than HDDs
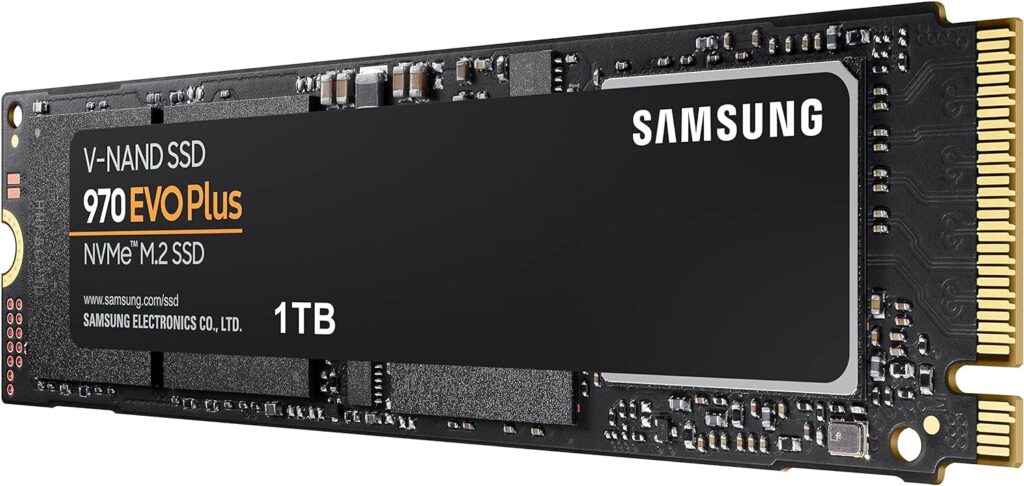
SSDs (Solid State Drives) generally surpass HDDs in speed due to their lack of moving parts. They use NAND flash memory for faster data access. Among SSDs, NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) drives stand out. NVMe SSDs, like the Samsung 970 Evo Plus, offer read speeds up to 3,500 MB/s and write speeds up to 3,300 MB/s.
NVMe SSD is the Fastest
SATA SSDs, while faster than traditional HDDs, lag behind NVMe SSDs. For instance, the Samsung 860 Evo offers read speeds of up to 550 MB/s and write speeds of up to 520 MB/s the Samsung 970 Evo Plus, blows it away with read speeds up to 3,500 MB/s and write speeds up to 3,300 MB/s.
| Drive Type | Example Model | Read Speed | Write Speed | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVMe SSD | Samsung 970 Evo Plus | 3,500 MB/s | 3,300 MB/s | PCIe |
| SATA SSD | Samsung 860 Evo | 550 MB/s | 520 MB/s | SATA |
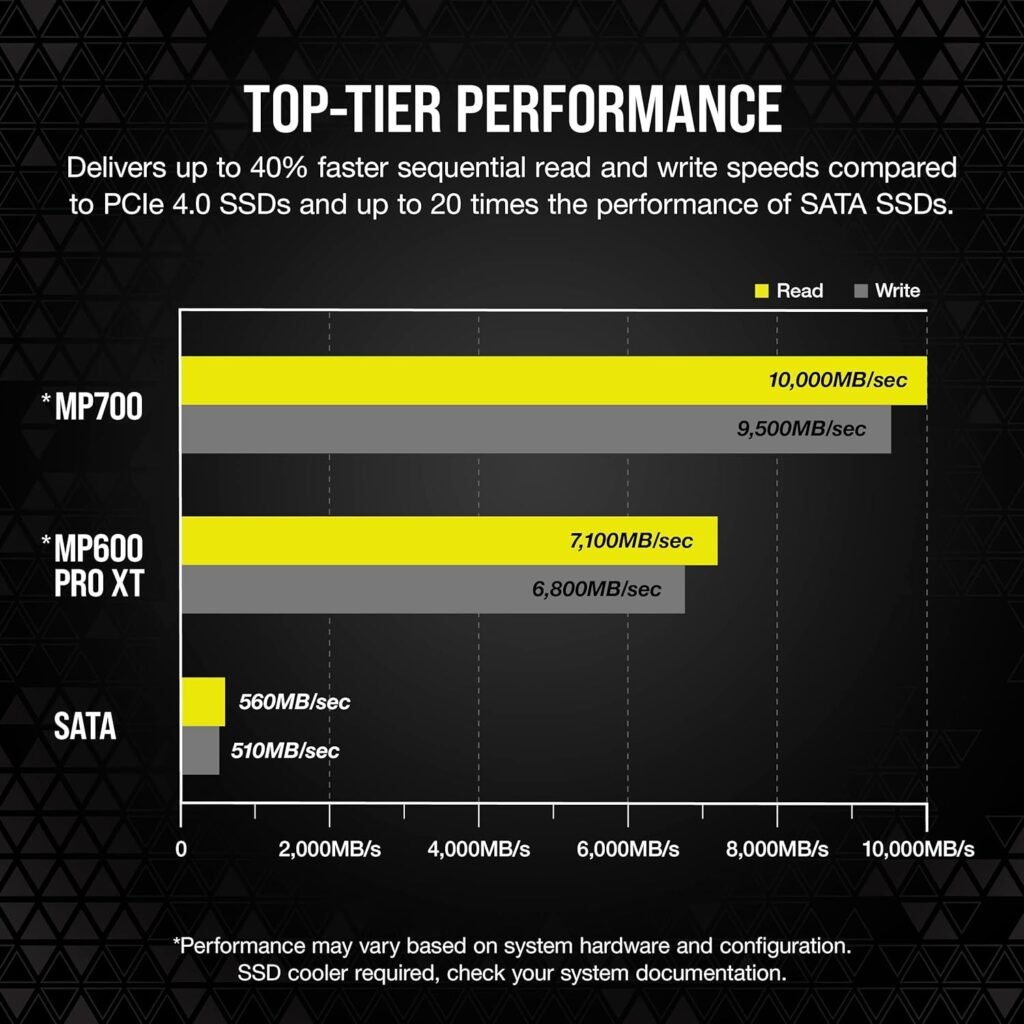
Gen 5 NVMe Performance Comparison
A Gen 5 NVMe SSD (Solid State Drive) can deliver up to 10,000MB/sec sequential read and up to 9,500MB/sec sequential write.
This NVMe requires a motherboard slot and will run very hot but will reward you with blistering performance.
The Corsair MP700 1TB SSD is available on Amazon for £155.98.
HDDs Are Slower But Reliable
HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) are not designed for speed but for capacity. However, some HDDs deliver respectable speeds.
High-Performance HDDs
The Western Digital Black series offers enhanced performance with read/write speeds of up to 180 MB/s due to a high spin rate (7,200 RPM) and additional cache.
The Seagate Enterprise Performance 15K offers read/write speeds of up to 233 MB/s.
While slower than SSDs, such HDDs are useful for bulk storage with reasonable performance.
| Drive Type | Example Model | Read Speed | Write Speed | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7200 RPM HDD | WD Black | 180 MB/s | 180 MB/s | SATA |
| 15,000 RPM HDD | Seagate Enterprise Performance | 233 MB/s | 233 MB/s | SATA |
Is an NVMe better than SSD?
Yes, and with a 1TB NVMe drive available for around £80 it’s the best disk choice if it fits in your machine.
What is the main difference between SSDs and HDDs?
SSDs (Solid State Drives) use flash memory to store data, offering faster read/write speeds, while HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) use magnetic storage platters and are generally slower but offer larger capacities at a lower cost.
Why are SSDs faster than HDDs?
SSDs lack moving parts and use flash memory, which allows for quicker data access and retrieval compared to the mechanical components of HDDs. NVMe SSDs, in particular, provide even faster speeds due to their advanced interface.
Are SSDs more durable than HDDs?
Yes, SSDs are generally more durable since they have no moving parts, reducing the risk of mechanical failure. This makes them less susceptible to physical damage compared to HDDs, which have delicate spinning platters.
Which is better for gaming: SSD or HDD?
An SSD is better for gaming due to its faster load times, which can significantly improve game performance and reduce lag during gameplay. However, an HDD can be useful for storing large game libraries due to its higher capacity.
Reliability of your new hard disk is your number one consideration, and with that in mind, it’s good practice to start with a well know reliable brand.