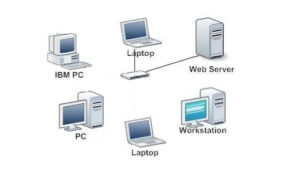
Network Hubs and Switches
In the intricate world of computer networking, a switch plays a pivotal role, often going unnoticed despite its critical function. Essentially, a switch serves as a control mechanism, directing the flow of data across a network by processing and forwarding information to the correct destination. It’s a fundamental component that ensures efficient data transfer, making it indispensable in both home and corporate networks.
Unlike a simple hub, which broadcasts data to all connected devices, a switch intelligently identifies the intended recipient of each data packet and sends it directly to that device. This not only increases the speed of the network but also enhances security and efficiency. Understanding how switches contribute to network performance and reliability can provide valuable insights into the seamless operation of modern digital communications.
How does a switch differ from a hub?
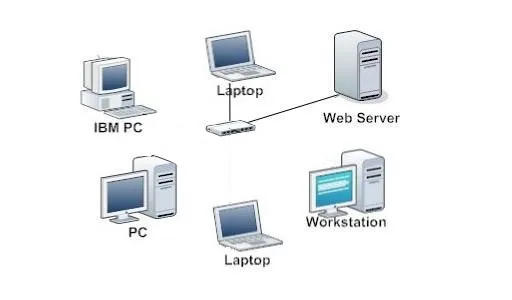
Hub Network
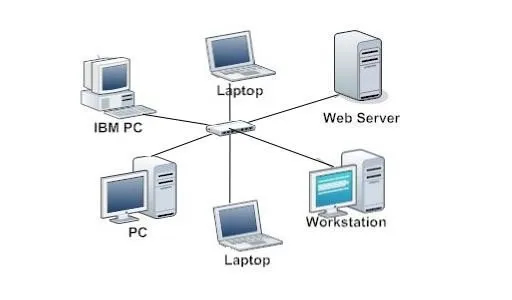
Switched Network
As outlined in the previous sections, both switches and hubs are integral devices for networking, but they operate differently, impacting their functionality and network efficiency. A key distinction lies in the mechanism each device uses to handle data packets.
A switch operates intelligently by examining data packets and routing them specifically to the designated devices on a network. It uses the MAC (Media Access Control) address inherent in each incoming packet to make precise delivery decisions. Once a switch determines the appropriate destination device for a packet, it sends the packet directly to that device only. This targeted approach conserves bandwidth and enhances the security and speed of the network.
Hubs, on the other hand, function in a more simplistic manner. Unlike switches, hubs do not analyze the data they receive. Instead, when a hub receives a data packet, it broadcasts the packet to every device connected to it, regardless of the recipient. This method can lead to significant network traffic and inefficiencies, as each device connected to the hub must process and discard packets not intended for it. Moreover, because all data is shared among all devices, network security could be compromised, making hubs less suitable for environments requiring confidentiality.
Another difference between these two networking devices is in their performance capabilities. Switches generally support full-duplex data transmission, allowing devices to send and receive data simultaneously. In contrast, hubs support half-duplex communication, where data can only flow in one direction at a time, which can further slow down the network.
The replacement of hubs by switches in many networks underscores a shift towards more efficient, secure, and faster networking solutions that are capable of handling the increased data loads of modern network environments.
Choosing a network Switch
The first decision to be made when selecting a Network Switch is the level of management required – basically none, some or all.
Unmanaged Switches: Commonly used in small networks or situations where basic connectivity is sufficient, unmanaged switches operate right out of the box. They require no configuration and automatically manage the data types and access, providing devices with direct connectivity to the network.
Managed Switches: Offering greater control, managed switches allow network managers to configure, manage, and monitor the network, enhancing network traffic control and security. Features include VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), QoS (Quality of Service) prioritisation, and SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) monitoring. These switches are ideal for enterprise networks needing high levels of data management and security.
Smart Switches: Positioned between unmanaged and managed, smart switches provide some management features for QoS and VLANs but with limited depth compared to managed switches. They’re suitable for businesses that require more control over their network than unmanaged switches offer but don’t need all functionalities of managed switches.
What is an unmanaged switch?
An unmanaged switch operates as a simple connectivity device in network setups. It enables various devices like computers, printers, and servers to communicate with each other within a Local Area Network (LAN) without manual intervention to manage settings or options. This type of switch does not allow any modifications to its factory settings, making it a plug-and-play device ideal for straightforward networking needs.
Typically, unmanaged switches are used in smaller networks or home offices where simplicity and low cost are prioritized over flexibility. They lack the advanced features found in managed switches, such as VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), QoS (Quality of Service) prioritization, and network management. However, they provide essential functions that facilitate the direct flow of data between devices.
When comparing unmanaged switches to their managed counterparts, it’s clear that they offer fewer controls. This trait reduces the complexity and setup time, providing an attractive solution for users who require basic network connectivity without the necessity for extensive configuration tasks or ongoing management.
Furthermore, their affordability makes unmanaged switches a popular choice for budget-conscious individuals or organizations. They are highly effective at handling data transmission within small networks, ensuring that all connected devices can access shared resources and communicate effectively.
By enhancing user experience through seamless operation and minimal maintenance requirements, unmanaged switches serve a critical role in numerous networking scenarios where advanced features are unnecessary.
What is a managed switch?
Understanding the role and functionality of computer switches is crucial for anyone involved in network setup or management. While unmanaged switches offer a straightforward solution for simple networks it’s the managed switches that bring in-depth control and adaptability to complex networking environments. These switches allow network managers to configure monitor and secure networks precisely ensuring efficient data handling and enhanced security protocols. As technology evolves the significance of choosing the right type of switch based on specific network requirements cannot be overstated. Whether it’s for a small home office or a large enterprise the right switch can dramatically influence the performance and reliability of a network.
Switched Network FAQ
What is the main difference between a network switch and a hub?
A network switch intelligently directs data to specific devices using MAC addresses, which enhances efficiency and security by avoiding universal data broadcasting like a hub does. This functionality supports full-duplex data transmission, providing increased speed and security over hubs.
Why are switches considered better than hubs in computer networking?
Switches are superior to hubs because they offer full-duplex data transmission, allowing for simultaneous data sending and receiving, which increases network speed and decreases data collisions. Additionally, they enhance network security by directing data to intended devices rather than broadcasting it to all connected devices.
What are unmanaged switches and who should use them?
Unmanaged switches are basic network switches that do not include advanced settings like VLANs or QoS, making them ideal for smaller networks or home offices where simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use are prioritised. They appeal to users who require straightforward, plug-and-play connectivity without the need for complex network management.
What advantages do unmanaged switches offer in a network setup?
Unmanaged switches provide seamless operation with minimal maintenance, focusing on direct data flow between devices with fewer controls. This simplicity reduces setup time and operational complexities, making them suitable for environments where advanced networking features are unnecessary. Their affordability also makes them an attractive option for basic connectivity needs.